From generations to generations media has been a help to us, whether its for entertainment to providing us informations, not just in our surroundings but in our studies and everyday life. Through media we can communicate with our loved ones in other places, but what we do not know is how did we get “media” in this technology world. From ancient time our way of communicating is through rocks to paper, and then it evolves through the years had passed. But what does Evolution of Media means?? Now we can find out.
First blog post
This is the post excerpt.
This is your very first post. Click the Edit link to modify or delete it, or start a new post. If you like, use this post to tell readers why you started this blog and what you plan to do with it.

Before & Now
Ways of Writing


As time passed, writings have changed into easier way…
To save some information as civilization transformed into more educated and more conducted era…
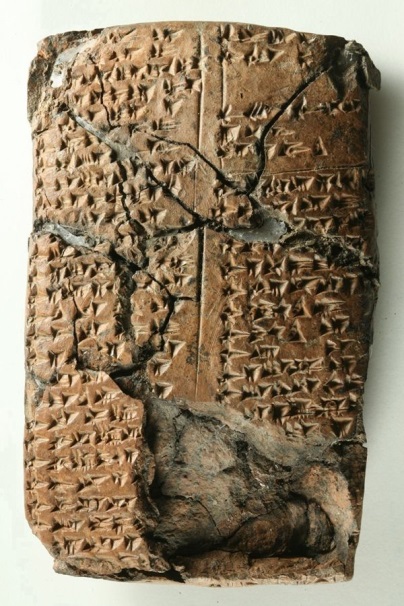

To clay tablet writings
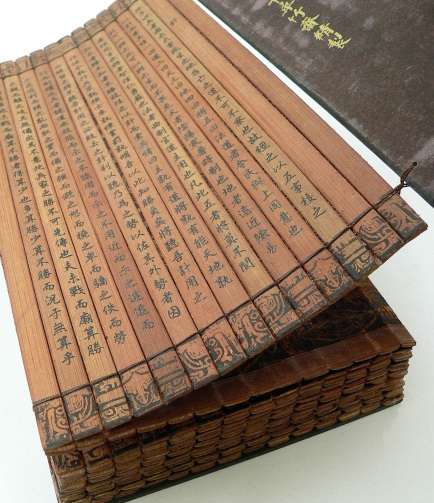

To wood
writings
 Paper/scroll writing, then it became a book.
Paper/scroll writing, then it became a book.
People always wonder how to write documents in a more faster and efficient way without wasting time and exhausting themselves out. To have more news and filing up documents, type writing machine was invented…

Writing articles and documents and serves as printing machine, it really saved the people from tiring their hand in writing and wasting a lot more time than usual. And so, it became a really popular way of writing.
Here comes the continuation…



















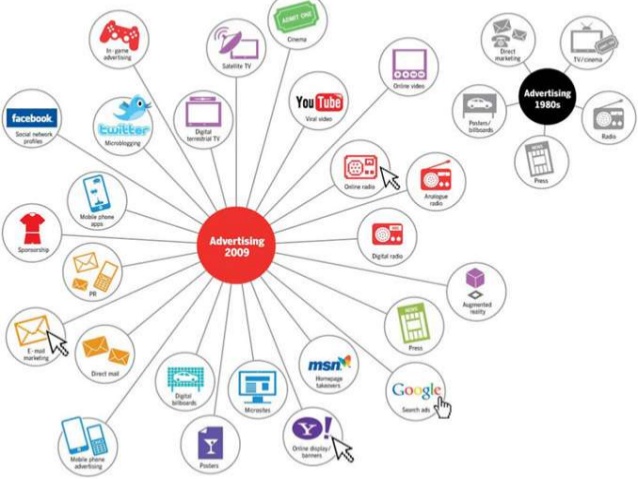
1.1 History of Media
In Ancient Times cave paintings, draw maps, and writings are the only way of communication then it evolved to rock, wood, leaves, and clay writings to papers or scrolls that ancient Egyptians and other dynasty used. Now we all have gadgets, internet and computers, but how did we get here?
Let’s take a sneak peek in our history:
Media History Timeline
(compiled by Prof. Jim McPherson, Whitworth College, 2002)
4000 B.C. – Sumerian stamp seals
3100 B.C. – Sumerian “writing” system on clay tablets
2000 B.C. – Phoenician alphabet
1900-1800 B.C. – Semitic alphabet in Egypt
600 B.C. – Egyptian papyrus scrolls
540 B.C. – Public library in Athens
105 A.D. – Chinese paper (didn’t arrive in West for centuries)
1450 – Gutenberg press (leads to Protestant Revolution, among other things)
1517 – Martin Luther nails “Ninety Five Theses” to church door in Wittenberg, Germany
1534 – first press in America (Spanish America)
1500s – Italian gazettes
1618 – Dutch Coranto (printed in English in 1620)
1638 – first press in what would become U.S. (Harvard College)
1644 – John Milton denounces licensing of the press in Areopagitica
1665 – Oxford Gazette (first English-language newspaper) in England
1690 – First American newspaper: Publick Occurrences (lasts one issue)
1704 – First successful American newspaper: The Boston News-Letter
1735 – John Peter Zenger trial
1741 – First American magazines
1783-1833 – Rise of Party Press
1791 – Bill of Rights (including First Amendment) ratified
1798 – Alien and Sedition Acts passed
1821 – Saturday Evening Post founded
1827 – First African-American newspaper in U.S.: Freedom’s Journal
1828 – First Native American newspaper in U.S.: Cherokee Phoenix
1828 – Noah Webster publishes first dictionary
1833s – New York Sun begins publication; rise of the Penny Press
1844 – Samuel Morse granted patent for telegraph. First message, May 24: “What hath God wrought?” Second message: “Have you any news?”
1848 – Associated Press founded
1860-1865 – Civil War brings home “necessity” of news
1877 – Thomas Edison invents the “talking machine”
1888 – Edison lab develops movie camera
1888 – George Eastman introduces the Kodak camera
1888 – Heinrich Hertz transmits wireless sound waves
1890 – Linotype machine introduced at newspapers
1891 –Edison patents Kinetoscope – first parlor opens 1894 in New York
1890s – first “New Journalism” period; “Yellow Journalism”
1890s – Edison develops mass market phonograph
1894 – Joseph Pulitzer’s New York World starts daily women’s page
1899 – “Stunt girl” Nellie Bly circles the world
1901 – Guglielmo Marconi sends and receives radio message across the Atlantic (Morse code, point to point)
1900s – Muckraking magazines
1905 – First “nickelodeon”
1906 – Reginald Fessenden broadcasts voice
1911 – Newsreels begin; continue into 1960s
1912 – Titanic sinks; leads to Federal Radio Act of 1912
1914-1918 – World War I propaganda, censorship, technology
1915 – D.W. Griffith releases Birth of a Nation, first full-length film to significantly impact culture
1917 – Charlie Chaplin becomes the first entertainer to earn $1 million
1919 – RCA founded
1920 – First radio stations in U.S. and Canada
1920s – “Jazz Journalism” tabloids
1922 – Reader’s Digest magazine founded
1923 – Lee de Forest shows first “talkie”
1923 – Time magazine debuts
1923 – A.C. Nielsen company begins
1923 – AT&T links two radio stations for first “network”
1927 – Federal Radio Act sets up commission to regulate airwaves
1927 – Philo Farnsworth applies for electronic TV patents
1927 – The Jazz Singer released
1928 – Academy Awards given for the first time (Wings wins Best Picture)
1930s & 40s – “Golden Age of Movies”
1933 – Eleanor Roosevelt insists on women-only press conferences (“the Roosevelt Rule”)
1934 – Federal Communications Commission (FCC) established
1936 – England is first country with regular TV broadcasts
1936 – Life magazine debuts
1938 – Orson Welles’ “War of the Worlds” broadcast
1939 – TV is a hit at the World’s Fair
1939 – First FM radio station started in New Jersey
1941 – First TV commercial advertises a Bulova clock
1941 – Welles’s Citizen Kane released; sometimes called the best movie of all time
1942 – John H. Johnson starts Negro Digest; would later found Ebony and Jet
1947 – Red Scare leads to congressional investigation of Hollywood
1948 – Supreme Court hands down Paramount Decision
1950 – Red Channels: The Communist Influence in Radio and Television ruins careers
1950s – “Golden Age of Television”
1951 – “I Love Lucy” debuts; uses film and three cameras
1952 – FCC lifts “the Freeze” imposed in 1948
1952 – Eisenhower runs 20-second campaign spot
1953 – TV Guide magazine debuts; Lucille Ball and her newborn son on first cover
1953 – Playboy magazine introduced; Marilyn Monroe is first centerfold
1954 – Edward R. Murrow’s “See It Now” focuses on Joseph McCarthy
1954 – Elvis Presley discovered by Sam Phillips of Sun Records
1958 – videotape introduced
1959 – Quiz show scandal rocks television industry
1960 – Kennedy-Nixon debate
1963 – Network news expands from 15 minutes to 30 minutes
1963 – Betty Friedan writes The Feminine Mystique
1964 – New York Times v. Sullivan gives press new right to criticize public officials
1964 – The Beatles first tour America
1965-1970s – Second “New Journalism” period; literary journalism; underground newspapers
1967 – Congress passes Public Broadcasting Act; PBS formed
Late 1960s – Internet formed for exchange of ideas, not available to general public
1969 – Neal Armstrong walks on moon; we see it on TV
1969 – ABC introduces made-for-TV movies
1970 – Feminists stage sit-in at Ladies Home Journal
1972 – Ms. magazine launched
1972 – Life magazine died; came back as monthly from 1978 to 2000
1972 – Boylan v. New York Times sex discrimination lawsuit filed
1972 – Cigarette advertising banned from TV
1974 – Richard Nixon resigns, a result of Watergate coverage
1974 – People magazine introduced
1975 – Home Box Office (formed by Time, Inc. in 1972) begins satellite distribution of TV; Ted Turner starts first “superstation”
1975 – Sony Betamax home videocassette recorder introduced
1976 – Matsushita introduces VHS
1978 – laser disc player introduced; largely a failure, but opened door for CDs
1979 – Sony Walkman appears in Japan
1979 – Iranian hostage crisis leads to “Nightline” and loss by Jimmy Carter to a former radio broadcaster and movie actor
1980 – “Who Shot J.R.?” on “Dallas” is first TV season-ending cliff-hanger
1981 – MTV (Music Television) first airs; first video is “Video Killed the Radio Star”
1982 – USA Today begins publication
1982 – Home shopping network debuts
1983 – Sony introduces CD player
1990s – Internet access opened to general public; changes everything
1996 – Telecommunications Act of 1996 brings V-chip, deregulation, and dramatic increase in mergers and takeovers
What events since 1996 would you add to this list?

